Primary hyperparathyroidism has some metabolic consequences in the calcium metabolism. Hypercalcemia in patient with primary hyperparathyroidism will resulted to the most important comorbidity that is chronic deposition of calcium in the kidney forming nephrolithiasis or other urolithiasis. It is not uncommon, patient with parathyroid adenoma come to health care professionals with the chief complain of recurrence nephrolithiasis.
Intrathyroidal parathyroid (IP) adenoma as a cause of primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT) presents a diagnostic challenge in localization and differentiating it from a thyroid nodule. We report the case of PHPT where preoperative imaging findings were compared with surgical and histopathological findings.
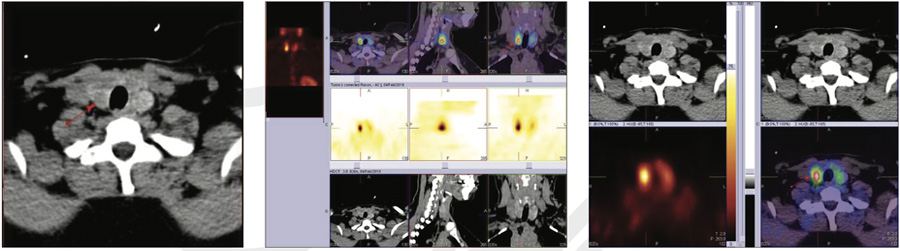
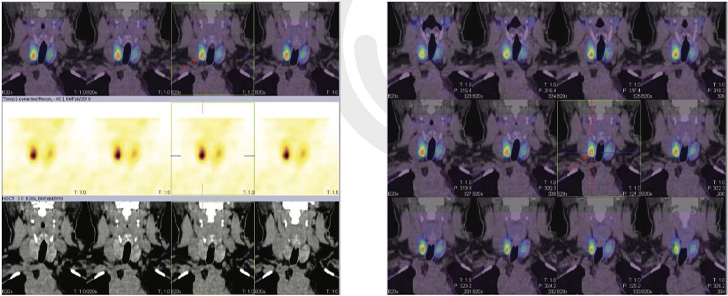
This case is a typical true IP adenoma (right lobe sub capsular) as diagnosed by preoperative 99mTc Sestamibi (Static and hybrid SPECT CT images) & 99mTc thyroid scan, with variation in Ultrasound and CT with contrast findings.
It is very essential that all the involved clinicians, radiologists, and surgeons are aware of the diagnostic features and pitfalls associated with IPs so as to enable a correct diagnosis and appropriate surgical or medical management.
48 years old female with history of recurrent renal stone formation and subsequently on investigation found to have found to have Hypercalcemia and Hyperparathyroidism.
Parathyroid hormone 107.8 pg/ml (15.0- 65.0 pg/ml), Serum Calcium 11.1 mg/dl (8.80 to 10.20 mg/dl).
Ultrasound of thyroid gland shows heterogeneous bulky thyroid gland revealing few nodules in both the lobes. Heterogeneous nodules noted abutting the posterior margin in left lobe of thyroid gland? Parathyroid adenoma.
CT scan of Neck with and without contrast showed a well-defined avidly enhancing ovoid mass is noted abutting the posterior aspect of left lobe of thyroid gland (15*14.5*28 mm), likely to be parathyroid origin adenoma and heterogeneous bulky thyroid noted.
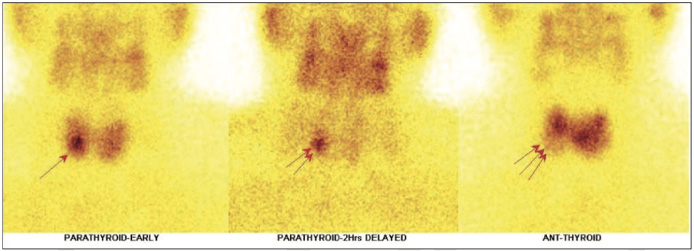
Shows focal area of abnormal MIBI tracer accumulation in lower third portion of the right lobe of thyroid gland on initial static (fig 1 arrow) and on adjunct SPECT-CT FUSED IMAGES (fig 3,4 arrow) and on delayed static images ( fig 1 arrow ), there is persistent tracer accumulation is seen in the same region
99mTc-Thyroid images shows, the right lobe measures 3.6*2.0 cms in size and left lobe 3.8*2.7 cms in size approximately with cold area in lower third portion of the right lobe (fig 2 arrow) and it is matching with hot area seen on MIBI parathyroid images, while rest of the gland shows relatively inhomogeneous tracer uptakes.
IN VIEW OF HIGH PTH & CALCIUM LEVELS- Intrathyroidal parathyroid adenoma (1.4*0.9 centimetre in size approximately) in lower portion of right lobe of thyroid gland has been reported. Left lobe does not show any obvious cold area on Tc thyroid images nor any hot area on MIBI thyroid images.
Excised right thyroid subcapsular parathyroid mass-Features of hypercellular parathyroid gland consistent with an Adenoma. Excised left cervical para-carotid swelling attachment to thyroid by small cord- Features of parasitic nodule consistent with adenomatoid nodule of thyroid.
Incidence of intrathyroidal parathyroid (IPs) is 0.5%–4% (1,2,3). True IPs account for less than 1% cases (3) of hyperparathyroidism and are located completely within the thyroid gland, surrounded by thyroid parenchyma on all sides. There is no intervening thyroid capsule between the thyroid and parathyroid tissue. They result when the primordium of the parathyroid gets trapped into the thyroid during descent at the time of embryogenesis. As the inferior parathyroid have longer descent, they are more likely to get trapped; however, their site of entrapment in the thyroid varies. Recognition of the entity is important, both for localization of adenoma in primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT) and conversely to prevent inadvertent hypoparathyroidism at the time of thyroidectomy. Although primary Hyperparathyroidism (PHPT) is asymptomatic in most patients, its main clinical manifestation is nephrolithiasis.
In the current case, the patient had history of recurrent renal stone disease, increased serum calcium, parathormone levels and intrathyroidal parathyroid adenoma (right lobe subcapsular) on surgery.