PHemangiomas are the most common vascular benign tumors of the liver. They are usually cavernous in
nature, containing large vascular spaces which are partially or filled with blood. The majority occur singly
and can be quite large, are often asymptomatic, and can be found incidentally at surgery, autopsy, or
during diagnostic investigations for an unrelated problem. Since there is little or no functional
impairment, liver function tests are usually normal. Use of non-invasive techniques for accurate diagnosis
is desirable since biopsy can lead to significant internal hemorrhage.
Moreover, when the tumor is present in staging or in the follow-up of oncological patients, the
differentiation of hepatic hemangioma from hepatic metastatic diseases is a common clinical question.
Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and multiple helical computed tomography (CT)
is also limited to distinguish focal hepatic lesions in some ways.
99mTc-labeled red blood cell scintigraphy through SPECT-CT hybrid imaging is non-invasive & highly
specific for the diagnosis of hepatic hemangiomas, which in turn able to avoid invasive method or biopsy.
34 years old lady.
Ref for 99mTc-RBC liver blood pool scan for the suspected hepatic hemangioma.
99mTc-RBC labelled liver blood pool SPECT-CT FUSED images shows large sized (7.1*6.4 cms) focal area of
RBC localization in VII segment of right lobe of liver postero-superiorly, which favoring liver hemangioma.
69 years old gentleman.
Ref for 99mTc-RBC liver blood pool scan for the suspected hepatic hemangioma on CT scan of abdomen
with and without contrast (6.5 cms sized lesion in left lobe segment four & shows centripetal
enhancement in the post contrast examination- may suggest atypical hemangioma. Smaller lesion
adjacent to the same in segment two with similar enhancement features).
99mTc-RBC labelled liver blood pool SPECT-CT FUSED images shows NO abnormal RBC pooling of the tracer seen in suspected underlying lesions and hence negative for hepatic hemangiomas.
Subsequently Alpha Feto Protein 9661 (0-5.0 IU/ml)- very high.
99mTc-RBC labelled liver blood pool SPECT-CT FUSED images shows focal area abnormal RBC pooling of the tracer seen in right lobe of liver favoring hepatic hemangioma.
As a non-invasive and highly specific method for diagnosing hepatic hemangioma, the 99mTc-labeled RBC liver blood pool (SPECT-CT) scintigraphy and can avoid invasive imaging or biopsy.
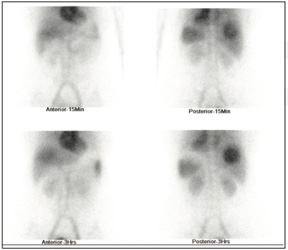
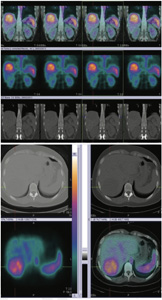
99mTc-RBC labelled liver blood pool SPECT-CT FUSED images shows large sized (7.1*6.4 cms) focal area of RBC localization in VII segment of right lobe of liver postero-superiorly, which favoring liver hemangioma.
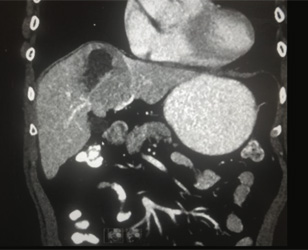
CT scan of abdomen with and without contrast 6.5 cms sized lesion in left lobe segment four & shows centripetal enhancement in the post contrast examination- may suggest atypical hemangioma. Smaller lesion adjacent to the same in segment two with similar enhancement features.
99mTc-RBC labelled liver blood pool SPECT-CT FUSED images shows NO abnormal RBC pooling of the tracer seen in suspected underlying lesions and hence negative for hepatic hemangiomas.
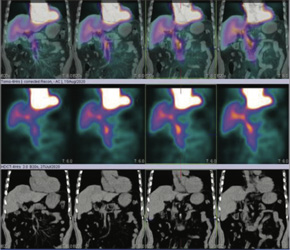
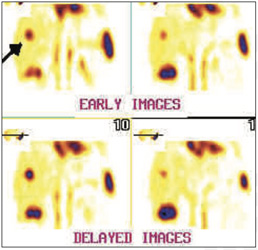
Right lobe Liver hemangioma