Bone scintigraphy are frequently performed as part of the diagnostic workup of osteomyelitis. Bone scintigraphy accurately diagnoses osteomyelitis in bones not affected by underlying conditions. Degenerative joint disease, fracture, and orthopedic hardware decrease the specificity of the bone scan, making it less useful in these situations.
Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone and may be localized or involve periosteum, cortex, marrow, and cancellous tissue. Acute osteomyelitis can arise hematogenous or through inoculation from direct trauma, a contiguous focus of infection, or sepsis following surgery.
Radiopharmaceuticals Single-Photon–Emitting Agents 99mTc-Diphosphonates Bone scintigraphy usually is performed with technetium-99mmethylene diphosphonate (99mTc-MDP). Uptake of this radiopharmaceutical, which binds to the hydroxyapatite crystal, depends on blood flow and rate of new bone formation.
When osteomyelitis is the indication, a Three-phase bone scanning has an accuracy of over 90% and is the radionuclide procedure of choice for diagnosing osteomyelitis in bone not affected by underlying conditions.
3-phase bone scan usually is performed. Three-phase bone scintigraphy consists of a dynamic imaging sequence, the flow or perfusion phase, followed immediately by static images of the region of interest, the blood pool or soft tissue phase. The third, or bone, phase consists of images of the area of interest, acquired 2-4 hours after injection. Focal hyper-perfusion, focal hyperemia, and focally increased bony uptake are the classic presentation of osteomyelitis on a 3-phase bone scan.
The test is both sensitive and specific for diagnosing osteomyelitis in bones not affected by underlying conditions.
17 years old boy with history of pain in left foot on and off for one year.
History of sports (football player) and juvenile Diabetes Mellitus & on injection insulin.
Diffuse marrow edema with smooth cortical thickening of the shaft of fifth metatarsal. A small rounded areas of hypo intensities on all sequences in in the mid shaft medullary cavity showing hyperintense rim on T1 weighted images suspicions for sequestrum favors chronic osteomyelitis involving the left 5th metatarsal bone (Differential diagnosis stress fracture appears less likely).
Referred for ISOTOPE THREE PHASE BONE SCAN FOR FURTHER WORK UP
Phase 1 (flow or perfusion) shows abnormally increased flow in 5th metatarsal region. Phase 2 (blood pool or soft tissue) shows abnormal pooling of tracer in 5th metatarsal region. Phase 3 (bone phase) shows abnormally increased tracer uptakes in 5th metatarsal bone of left foot (Better appreciated in SPECT CT fused images). The underlying CT images shows focal thickening of the shaft of 5th metatarsal bone with sclerosis of trabeculae
favors osteomyelitis of 5th metatarsal bone of left foot
8 years old boy with history of right leg pain swelling and difficulty in walking. CRP raised.
X-rays –unremarkable.
Phase 1 (flow or perfusion)- shows abnormally increased flow in proximal 2/3rd portion of right tibia. Phase 2 (blood pool or soft tissue) -shows abnormal pooling of tracer in the same region. Phase 3 (bone phase) shows abnormally increased tracer uptakes in proximal two third portion of shaft of right tibia (more so focal in upper portion & could be the focus of infection), favors osteomyelitis involving proximal 2/3rd of right tibia shaft.
10 years old boy with pain and clicking sensation in right knee.
CRP raised.
X-rays-unremarkable.
Phase 1 (flow or perfusion)- shows abnormally increased flow in metaphyseal area of right femur. Phase 2 (blood pool or soft tissue)- shows abnormal pooling of tracer in the same area. Phase 3 (bone phase) shows abnormally increased tracer uptakes in metaphyseal region of the right femur favors osteomyelitis involving metaphyseal of the right femur
Surgery- Right metaphyseal osteomyelitis extending to knee.
45 years old female with pain and swelling over left foot laterally.
CRP raised.
X-rays-unremarkable.
Phase 1 (blood pool or soft tissue)- shows abnormal pooling of tracer in the left fifth metatarsal bone distally of left foot. Phase 2 (bone phase) shows abnormally increased tracer uptakes in left fifth metatarsal bone distally of left foot, favors osteomyelitis involving fifth metatarsal bone distally of left foot.
Surgery: left fifth meta-tarsal bone osteomyelitis distally.
3 years old female with history of fall in school, followed by limping of right lower limb with restricted movement.
Subsequently developed fever & pain in right Knee.
CRP 27 (0-10), ESR 50 (0-20), WBC 11.3
Initially treated with antibiotics for week.
Phase 1 (blood pool or soft tissue)- shows abnormal pooling of tracer in right epiphyseal regions of both femur and tibia. Phase 2 (bone phase) shows abnormally increased tracer uptakes in right knee involving epiphyseal region of femur and tibia, favors inflammatory/infective pathology of Right knee involving both epiphyseal of femur & tibia and possibility of septic arthritis is more likely.
Right knee arthroscopy-Lot of synovitis with frank pus.
History of slowly growing swelling since last one and half years and recently become more progressive, which painful and tender.
Phase 1 (blood pool or soft tissue)-shows abnormal pooling of tracer in left clavicular in medial half. Phase 2 (bone phase) shows abnormally increased tracer uptakes in right clavicle in medial half, favors possibility of infective pathology.
Biopsy- Left clavicle tuberculosis.
Bone scintigraphy in tuberculous spondylodiscitis, European Spine Journal 8(3):205-9, February 1999
Hemant pandit, P.D. Bhonsale, Shekhar V Shikare, S.Y Bhojraj
Phase 1 (flow or perfusion) shows abnormally increased flow in 5th metatarsal region. Phase 2 (blood pool or soft tissue) shows abnormal pooling of tracer in 5th metatarsal region. Phase 3 (bone phase) shows abnormally increased tracer uptakes in 5th metatarsal bone of left foot (Better appreciated in SPECT CT fused images). The underlying CT images shows focal thickening of the shaft of 5th metatarsal bone with sclerosis of trabeculae favors osteomyelitis of 5th metatarsal bone of left foot.
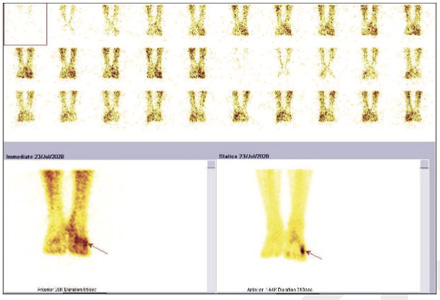
Fig 1: 3-Phase bone scan (left foot)
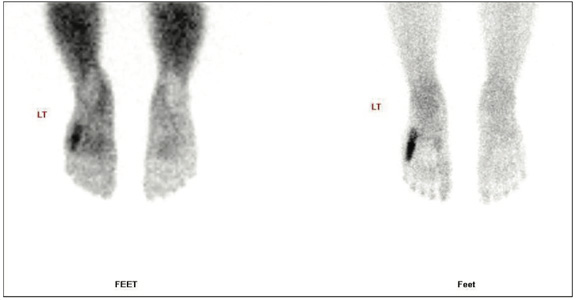
Fig 2: Blood pool & bone images of foot
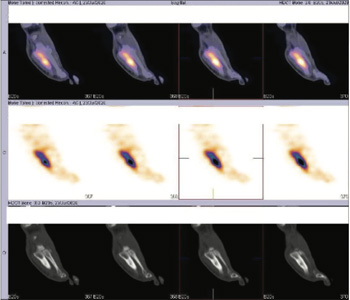
Fig 3: SPECT CT fused images of left foot (sag view)
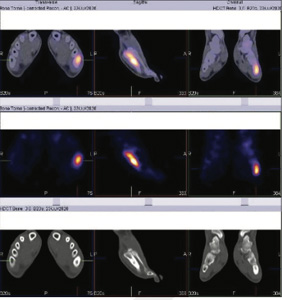
Fig 4: SPECT CT fused images of left foot (three views)
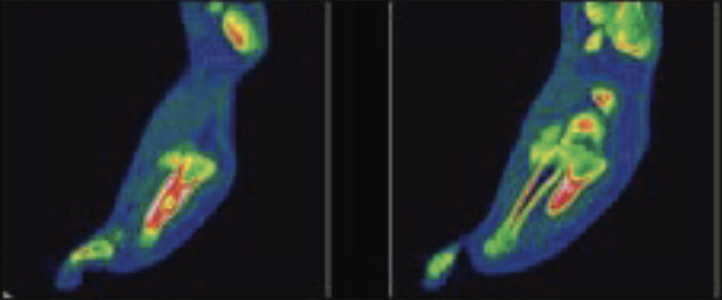
Fig 5: CT scan images of left foot
Phase 1 (flow or perfusion)- shows abnormally increased flow in proximal 2/3rd portion of right tibia. Phase 2 (blood pool or soft tissue) -shows abnormal pooling of tracer in the same region. Phase 3 (bone phase) shows abnormally increased tracer uptakes in proximal two third portion of shaft of right tibia (more so focal in upper portion & could be the focus of infection), favors osteomyelitis involving proximal 2/3rd of right tibia shaft.
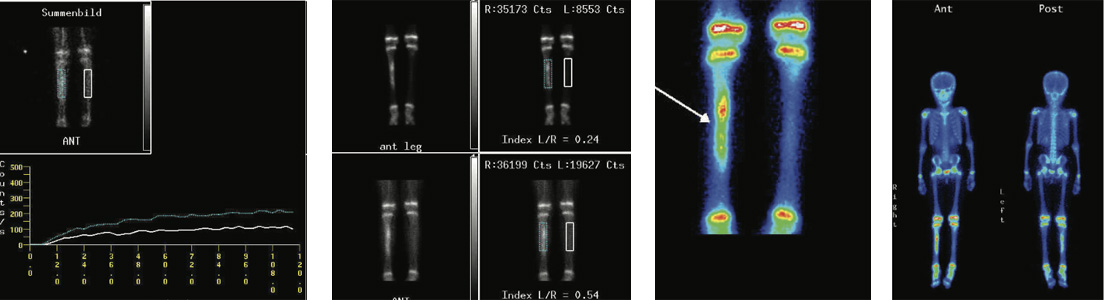
Fig 1: Phase 1 (flow images)
Fig 2: Phase 2 (blood pool Images) upper rowPhase 3 (bone images)- lower row
Fig 3: Phase 3 (Bone images)
Fig 4: Phase 3 (Bone images)
Phase 1 (flow or perfusion)- shows abnormally increased flow in metaphyseal area of right femur. Phase 2 (blood pool or soft tissue)- shows abnormal pooling of tracer in the same area. Phase 3 (bone phase) shows abnormally increased tracer uptakes in metaphyseal region of the right femur favors osteomyelitis involving metaphyseal of the right femur.
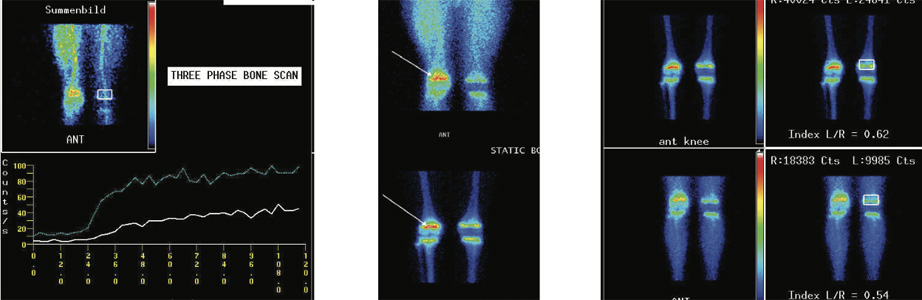
Fig 1: Phase 1 (flow images)
Fig 2: Phase 2 (blood pool Images)-upper row Phase 3 (bone images)- lower row
Fig 3: Phase 3 (Bone images)
Phase 1 (blood pool or soft tissue)-shows abnormal pooling of tracer in the left fifth metatarsal bone distally of left foot.Phase 2 (bone phase) shows abnormally increased tracer uptakes in left fifth metatarsal bone distally of left foot, favors osteomyelitis involving firth metatarsal bone distally of left foot.
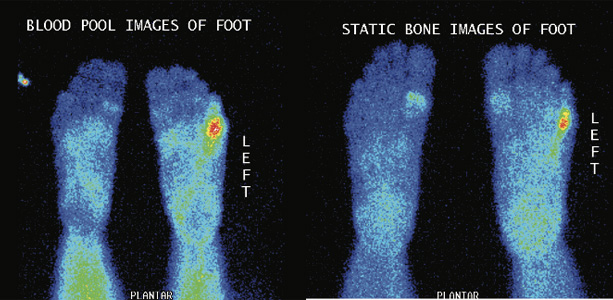
Fig 1 Phase 2 (blood pool Images)-upper row Phase 3 (bone images)- lower row
Phase 1 (blood pool or soft tissue)- shows abnormal pooling of tracer in right epiphyseal regions of both femur and tibia. Phase 2 (bone phase) shows abnormally increased tracer uptakes in right knee involving epiphyseal region of femur and tibia, favors inflammatory/infective pathology of Right knee involving both epiphyseal of femur & tibia (septic arthritis is more likely).
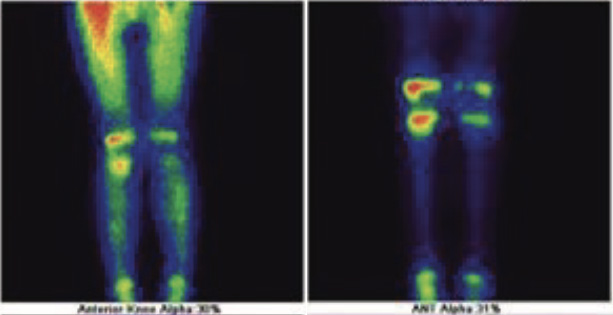
Fig 1: Phase 2 (blood pool Images) -upper row Phase 3 (bone images)- lower row
Phase 1 (blood pool or soft tissue)- shows abnormal pooling of tracer in left clavicular in medial half. Phase 2 (bone phase) shows abnormally increased tracer uptakes in right clavicle in medial half, favors possibility of infective pathology.
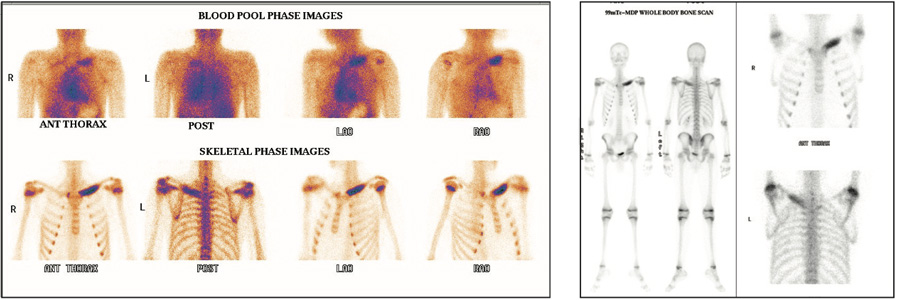
Fig 1: Phase 2 (blood pool Images)- upper row Phase 3 (bone images)- lower row
Fig 2: Phase 3 (Bone images)