Pain about the foot and ankle can prove a diagnostic challenge given the complex anatomical relations and structural mechanics. An accurate history and clinical examination may need to be complemented by an array of imaging modalities to provide a sound basis for diagnosis and subsequent treatment. Imaging of the foot is usually achieved by plain radiography, ultrasound, computerized tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).Disturbances in the function or metabolism of the local tissues utilizes nuclear medicine techniques such as a radio-labelled bone scan. This SPECT CT hybrid imaging or co-registration is well recognized as enhancing the diagnostic powers of each modality. The SPECT-CT combines a multi head gamma-camera and CT scanner mounted together with a common imaging table. Administration of the radiopharmaceutical is followed by a standard bone scintigraphy protocol including the early blood pool imaging at 5 min followed by the delayed planar views. The co-registered SPECT-CT scan is obtained during this time without the patient leaving the table.
27 years old gentleman with history of pain in right ankle region. MRI right ankle- Osteo-arthritic changes at the medial compartment of the sub-talar joint (old trauma sequelae).
99mTc MDP BONE SCAN of Ankle and foot
Blood pool phase-Abnormal focal pooling of tracer seen in right ankle region (fig 1) Bone phase (Static & SPECT CT fused images of ankle & foot)- Focally increased tracer uptake in right talo-calcaneal articulation favors active osteoarthritis (figure 1,2,3).
19 years old lady with history of with pain in foot on walking. Suspected to have Stress fracture or AVN of navicular bone of left foot. Referred for isotope bone scan.
99mTc MDP BONE SCAN of Ankle and foot
BONE SCAN SPETC-CT fused images of ankle & foot- Focally increased tracer uptake seen in the adjoining region of navicular and accessory navicular bone on either side (left >right) favors the possibility of navicular syndrome (figure 2,3).
Navicular syndrome- People who have accessory navicular often are unaware of the condition. However, some people with this extra bone develop painful condition known as accessory navicular syndrome.
As bone scintigraphy provides metabolic information, it can help to find the origin of pain, and SPECT/CT can further improve the specificity by adding anatomical information. SPECT-CT does have a role in clarifying or establishing a diagnosis in obscure foot and ankle pain.
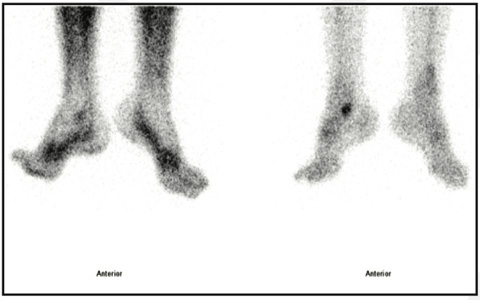
Fig 1: 99mTc MDP Blood pool & static bone images of foot
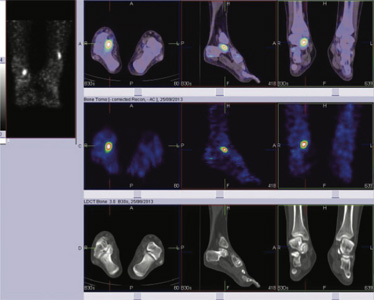 Fig 2: 99mTc MDP SPECT CT FUSED bone images of foot
Fig 2: 99mTc MDP SPECT CT FUSED bone images of foot
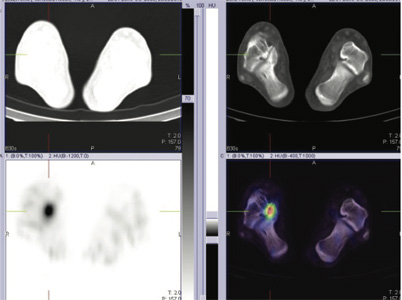
Fig 3: 99mTc MDP SPECT CT FUSED bone images of foot
99mTc MDP BONE SCAN of Ankle and foot Blood pool phase-Abnormal focal pooling of tracer seen in right ankle region. Bone phase (Static & SPECT CT fused images of ankle & foot)- Focally increased tracer uptake in right talo-calcaneal articulation favors active osteoarthritis.
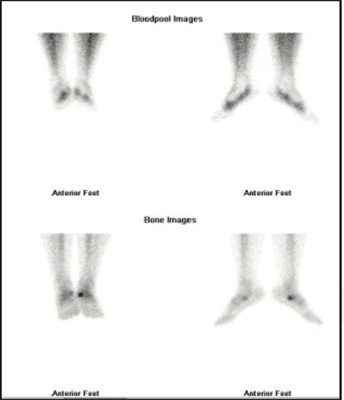
Fig 1: 99mTc MDP Blood pool & static bone images of foot
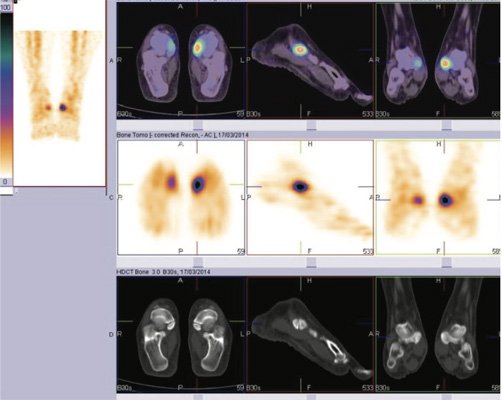
Fig 2: 99mTc MDP SPECT CT FUSED bone images of foot
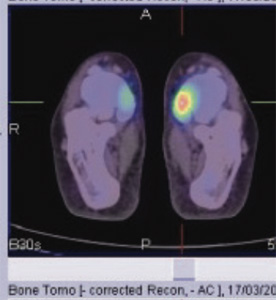
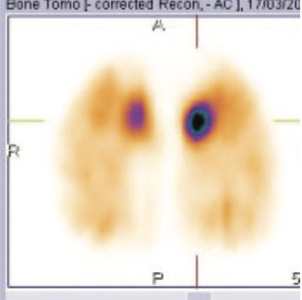
Fig 3, 4 & 5: 99mTc MDP SPECT CT FUSED bone images of foot
BONE SCAN SPETC-CT fused images of ankle & foot- Focally increased tracer uptake in the adjoining region of navicular and accessory navicular bone on either side (left>right), favours the possibility of navicular syndrome.
Navicular syndrome- People who have accessory navicular often are unaware of the condition. However some people with this extra bone develop painful condition known as accessory navicular syndrome.